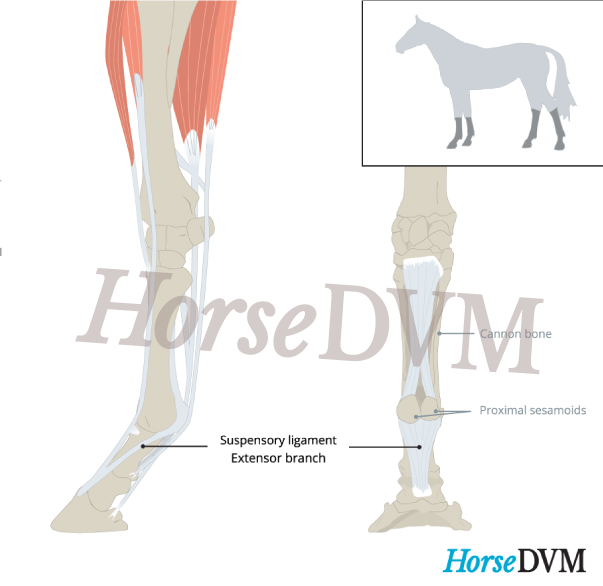
Suspensory ligament branch desmitis is a specific type of injury to the horse's suspensory ligament which involves damage to medial and/or lateral branch region, occurring in the forelimbs or hind limbs. Typically only a single branch in a single limb is affected, however both can be affected, especially in the hindlimbs.
Injures to the suspensory ligament branches frequently occur as an acute incident consequent to abnormal overloading. In most instances, there is an underlying condition that is causing repetitive stress and weakening of the tissues before development of lameness.
The treatment prescribed by your veterinarian will depend on the function of the horse, severity of the injury, clinical signs, and history of the horse. Suspensory ligament branch injuries have a high rate of recurrence and often become chronic, and they are frequently accompanied by osteoarthritis of the fetlock joint (osslets), which itself can become performance limiting in many sport horses.