Black locust (
Robinia pseudoacacia) is a perennial shrub or medium-sized, deciduous, fast-growing tree from the bean (Fabaceae) family. It is native to North America, and found growing in the Appalachian mountains from Pennsylvania to Alabama as well as parts of the Midwestern United States.
Black locust is often planted as an ornamental for landscaping, for its showy aromatic flowers. Identifying characteristics for black locust trees:
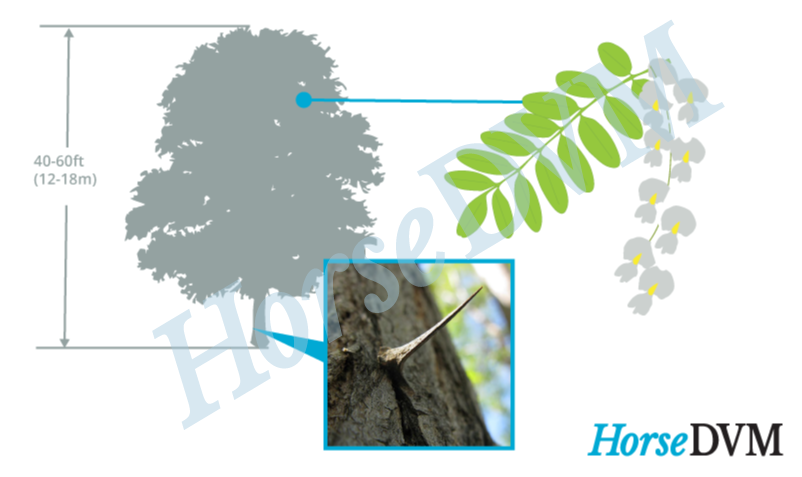
- Height: 40 to 80 feet tall
- Diameter: Mature trunks are usually 3 to 4 feet in diameter
- Bark: Reddish-brown to dark brown, slightly cracked, and furrowed on young trees. The bark becomes deeply furrowed on older trees.
- Twigs & Branches: The twigs may be slender or stout, and somewhat brittle. Pairs of stiff spines are found at the base of each leaf stalk (petiole) on younger branches, which can grow up to 1 inch in length. Shoots of young plants are zigzagged, green and smooth that turn red brown with age. Sharp spines develop in pairs, at the base of leaf petioles and stems; these will eventually turn into woody spines up to 1 in long. When cut, shoots will readily sprout from stumps.
- Flowers: Flowers are fragrant, white, pink or purple, medium-sized, and grow in long, drooping pea-like clusters from 4 to 8 inches long.
- Root system: Black locust roots spread laterally, just above the soil surface.
- Fruit: Large (2 to 4 inches long), flat, hairless, red to dark brown, thin pods appear in September, that contain four to eight kidney-shaped, brown seeds within each pod. Pods resemble a long, thin butterbeans. Fruits will often remain on tree branches until the following spring.
- Leaves: Alternately arranged along stems, medium to dark green in color, and divided into two rows of 7 to 19 leaflets. Individual leaves are elliptic to oval leaflets that are 8 to 14 inches long.
Toxic components
Black locust contains several lectins, which are a diverse group of proteins often found in plants as well as microorganisms that bind carbohydrates, precipitate glycoproteins, and agglutinate cells. The most important toxic constituents of the black locust tree are robin and robinin, which are large proteins called toxalbumins similar to ricin. The toxin is particularly prevalent in the inner bark, seeds, and leaves. Once the toxins are absorbed into the blood stream, rapid multi-system organ failure follows close behind. Symptoms of poisoning present 1-2 hours following ingestion of toxic quantities of black locust.
Most reported cases of poisoning involving horses were the result of horses eating the young shoots or chewing the bark from tree trunks. Ingestion of black locust tree parts causes
black locust toxicity in horses.
- Loss Of Appetite
- Diarrhea (possibly Bloody)
- Colic
- Weakness
- Depression
- Nervousness
- Jaundice
- Irregular Pulse
- Cold Extremities
- Dilated Pupils
- Tachycardia
FIRE CONTROL: Burning has not been effective in controlling black locust. Fire may kill main stems, but this will result in prolific sprouting. Fire also may stimulate seed germination and create favorable conditions for seedling establishment.
BIOLOGICAL CONTROL: Black locust suffers considerable damage from insects, particularly the black locust borer, Megacylline robinine.
CHEMICAL: Seedlings and trees less than 5 feet tall can be controlled with a broad-cast application of Crossbow® at 1.5 gal/A in 10 to 30 gallons of water per acre. Spot applications can be made with a high volume applicator and a 1% to 1.5% v/v mix. When using high volume applicators, apply to covering foliage and stems until the solution drips. For trees taller than 5 feet, control will be more difficult — use a basal or cut stump application. Repeated applications of glyphosate products can suppress black locust; however, misapplication may damage desirable forages. If applied in the pasture, you cannot treat more than 10% of an acre using a rate of 2 qts/A. For tree control outside the harvested pasture, use 1.5 to 3 qts/A or 1% to 1.5% v/v mix in a high volume applicator. Dicamba products (Banvel®, Clarity®) can suppress black locust. Using 0.5, 1, or 2 lbs ai/A of dicamba requires waiting periods of 37, 51, or 70 days, respectively (see product label for exact rates and waiting periods). Make girdle or stump cut applications on trees using one part herbicide and one to three parts water.